Cute bird

Attitude is a manner of thinking, feeling, or behaving that reflects a state of mind. Attitude influences the behavior of the individuals. ~Dr Anil Kr Sinha
As a single footstep will not make a path on the earth, so a single thought will not make a pathway in the mind. To make a deep physical path, we walk again and again. To make a deep mental path, we must think over and over the kind of thoughts we wish to dominate our lives. ~Unknown
You must make use of our own mind and perception instead of always believing on what you hear. ~Anurag Prakash Ray
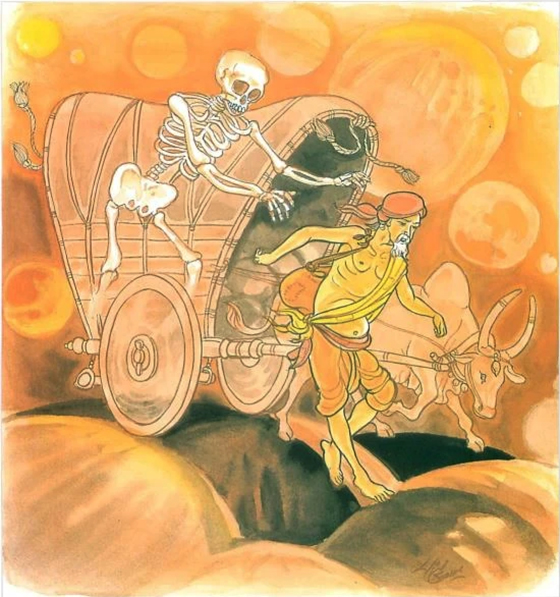


Verse 1: All mental phenomena have mind as their forerunner; they have mind as their chief; they are mind-made. If one speaks or acts with an evil mind, ‘dukkha’ 3 follows him just as the wheel follows the hoofprint of the ox that draws the cart.
manasa ce padutthena (Verse 1) and manasi ce pasannena (Verse 2): Manasa here means intention or volition (cetana); volition leads one to the performance of volitional actions, both good and evil. This volition and the resultant actions constitute kamma; and kamma always follows one to produce results. Cakkhupala’s blindness (Verse 1) was the consequence of his having acted with an evil intention in a previous existence and Matthakundali’s happy existence in Tavatimsa celestial world (Verse 2) was the result of his mental devotion (manopasada) to the Buddha.
dukkha: In this context, dukkha mens suffering, or physical or mental pain, misfortune, unsatisfactoriness, evil consequences, etc., and rebirth in the lower planes of existence or in the lower strata of human society if born in the human world.
The Story of Thera Cakkhupala
While residing at the Jetavana monastery in Savatthi, the Buddha uttered Verse (1) of this book, with reference to Cakkhupala, a blind thera. Continue reading
Suppose you go and sit in the middle of a freeway with the cars and trucks charging down at you. You can’t get angry at the cars, shouting, ”Don’t drive over here! Don’t drive over here!” It’s a freeway, you can’t tell them that. So what can you do? You get off the road! The road is the place where cars run, if you don’t want the cars to be there, you suffer.
It’s the same with sankhāras. We say they disturb us, like when we sit in meditation and hear a sound. We think, ”Oh, that sound’s bothering me.” If we understand that the sound bothers us then we suffer accordingly. If we investigate a little deeper, we will see that it’s we who go out and disturb the sound! The sound is simply sound. If we understand like this then there’s nothing more to it, we leave it be. We see that the sound is one thing, we are another. One who understands that the sound comes to disturb him is one who doesn’t see himself. He really doesn’t! Once you see yourself, then you’re at ease. The sound is just sound, why should you go and grab it? You see that actually it was you who went out and disturbed the sound.
This is real knowledge of the truth. You see both sides, so you have peace. If you see only one side, there is suffering. Once you see both sides, then you follow the Middle Way. This is the right practice of the mind. This is what we call straightening out our understanding. ~Ajahn Chah
The flowers of Dendrobium spectabile defy description. The bizarre 3-inch blossoms have sepals and petals that are extremely twisted — sometimes wrapping around each other and keeping the buds from opening. The colors are a blend of yellow, burgundy and white but give the impression of a washed-out tan. The throat has a “hinged” mechanism that bounces with air movement, attracting a specific pollinator in the wild. The grower can simulate this bounce by gently shaking the flower. The blooming duration is about six weeks, and older plants can easily produce 100 blossoms or more.
Fragrance is a highly coveted trait in orchids, though few genera offer it. This Aussie Dendrobium’s semi-sweet aroma is strong from across the room, day or night. Even Oncidium Sharry Baby, the famous chocolate-scented Dancing Lady, cannot compete with the intensity.
Source: Richmond Times-Dispatch, by Arthur Chadwick
Suppose one morning you’re walking to work and a man yells abuse and insults at you from across the street. As soon as you hear this abuse your mind changes from its usual state. You don’t feel so good, you feel angry and hurt. That man walks around abusing you night and day. Whenever you hear the abuse, you get angry, and even when you return home you’re still angry because you feel vindictive, you want to get even.
A few days later another man comes to your house and calls out, ”Hey! That man who abused you the other day, he’s mad, he’s crazy! Has been for years! He abuses everybody like that. Nobody takes any notice of anything he says.” As soon as you hear this you are suddenly relieved. That anger and hurt that you’ve pent up within you all these days melts away completely. Why? Because you know the truth of the matter now. Before, you didn’t know, you thought that man was normal, so you were angry at him. Understanding like that caused you to suffer. As soon as you find out the truth, everything changes: ”Oh, he’s mad! That explains everything!”
When you understand this you feel fine, because you know for yourself. Having known, then you can let go. If you don’t know the truth you cling right there. When you thought that man who abused you was normal you could have killed him. But when you find out the truth, that he’s mad, you feel much better. This is knowledge of the truth.
~Ajahn Chah
At least 85 people have been killed and around one hundred injured, after a cooking gas cylinder blew up in a crowded restaurant in central India.

These words ‘the Middle Way’ do not refer to our body and speech, they refer to the mind. When a mental impression which we don’t like arises, it affects the mind and there is confusion. When the mind is confused, when it’s ‘shaken up’, this is not the right way. When a mental impression arises which we like, the mind goes to indulgence in pleasure – that’s not the way either.
We people don’t want suffering, we want happiness. But in fact happiness is just a refined form of suffering. Suffering itself is the coarse form. You can compare them to a snake. The head of the snake is unhappiness, the tail of the snake is happiness. The head of the snake is really dangerous, it has the poisonous fangs. If you touch it, the snake will bite straight away. But never mind the head, even if you go and hold onto the tail, it will turn around and bite you just the same, because both the head and the tail belong to the one snake.
In the same way, both happiness and unhappiness, or pleasure and sadness, arise from the same parent – wanting. So when you’re happy the mind isn’t peaceful. It really isn’t! For instance, when we get the things we like, such as wealth, prestige, praise or happiness, we become pleased as a result. But the mind still harbours some uneasiness because we’re afraid of losing it. That very fear isn’t a peaceful state. Later on we may actually lose that thing and then we really suffer. ~Ajahn Chah